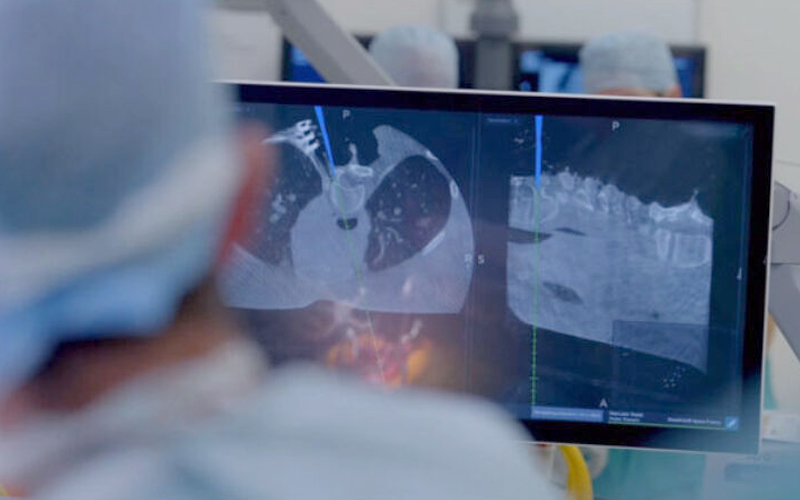
Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM)
Intraoperative Neuromonitoring (IONM) is an advanced technique used during brain and spine surgeries to continuously monitor the function of the nervous system in real time.
Its primary goal is to help the surgical team detect and prevent potential damage to critical structures such as the brain, spinal cord, and major nerves while operating.
By using IONM, neurosurgeons can perform complex procedures with greater precision and safety, reducing the risk of long-term neurological deficits such as weakness, speech problems, or loss of sensation.
Importance of IONM
The brain and spinal cord are delicate and densely packed with pathways that control movement, sensation, speech, and vital body functions.
During surgery—especially for brain tumours, skull base lesions, spinal cord tumours, aneurysms, or deformity corrections—even a small shift or manipulation may put these pathways at risk.
IONM acts like an early warning system, allowing the surgical team to:
-
Detect changes in nerve function instantly.
-
Adjust surgical technique in real time to prevent permanent damage.
-
Improve surgical outcomes while maintaining patient safety.
How IONM Works
IONM uses electrical impulses and specialized monitoring equipment to check the activity of the nervous system during surgery.
Key steps include:
-
Pre-Surgery Setup: Special electrodes are placed on the scalp, face, limbs, or inside the muscles.
-
Monitoring During Surgery: The electrodes send and record signals from the brain, spinal cord, or nerves while the patient is under anesthesia.
-
Real-Time Feedback: A neurophysiologist and the surgical team track these signals throughout the procedure to ensure vital pathways remain intact.
Types of Monitoring Techniques
We use a range of techniques tailored to the type of surgery:
-
Somatosensory Evoked Potentials (SSEP): Monitors sensory nerve pathways from limbs to the brain.
-
Motor Evoked Potentials (MEP): Checks the motor pathways that control muscle movement.
-
Electromyography (EMG): Detects nerve irritation or injury during surgery.
-
Electroencephalography (EEG): Monitors brain electrical activity and detects changes in brain perfusion.
-
Brainstem Auditory Evoked Potentials (BAEP): Used in surgeries near the auditory nerve or brainstem.
-
Cranial Nerve Monitoring: Protects critical nerves responsible for facial movement, speech, swallowing, and vision.
Surgeries That Benefit from IONM
IONM is particularly valuable in the following procedures:
-
Brain tumour and skull base tumour surgeries.
-
Surgery for vascular lesions such as aneurysms or AVMs.
-
Spine and spinal cord tumour surgeries.
-
Correction of spinal deformities (e.g., scoliosis).
-
Pituitary gland and brainstem surgeries.
-
Removal of acoustic neuromas or other cranial nerve-related tumours.
-
Complex trauma or re-operation cases where normal anatomy may be altered.
Benefits of IONM
-
Enhanced Safety: Reduces the risk of nerve damage during surgery.
-
Improved Outcomes: Helps preserve motor, sensory, and cognitive functions.
-
Real-Time Guidance: Allows surgeons to adapt their approach immediately if changes occur.
-
Better Recovery: Patients often experience fewer postoperative complications and a smoother recovery process.
Why Choose Our Centre for IONM-Assisted Surgeries
-
Experienced Neurosurgeon & Neuro-Oncosurgeon: Skilled in integrating IONM into delicate procedures.
-
Dedicated Neurophysiology Team: Trained specialists continuously monitor the patient throughout the surgery.
-
Advanced Technology: State-of-the-art IONM systems ensure precise and reliable monitoring.
-
Comprehensive Care: Multidisciplinary collaboration between neurosurgeons, anesthesiologists, and rehabilitation experts.
-
Focus on Patient Safety: Every procedure is planned and executed with the utmost care to protect neurological function.
Patient Experience
For the patient, IONM is non-invasive and painless. Electrodes are placed while the patient is under anesthesia, and no additional discomfort is involved.
This technology works silently in the background to help the surgical team deliver safer and more effective outcomes.