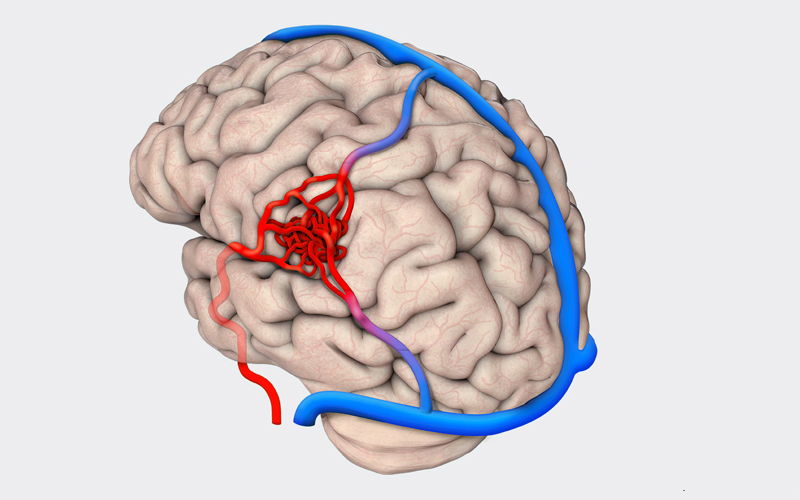
Brain Aneurysm & Arteriovenous Malformations
Brain Aneurysms and Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs) are serious conditions involving the blood vessels in the brain. Both can lead to life-threatening bleeding (hemorrhage) if not diagnosed and treated promptly.
-
A Brain Aneurysm is a weak, bulging area in a brain artery that can leak or rupture, causing sudden bleeding in or around the brain (subarachnoid hemorrhage).
-
An Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM) is an abnormal tangle of arteries and veins that disrupts normal blood flow and can rupture, leading to bleeding in the brain.
Advances in neurosurgery and neuro-interventional techniques now allow for early detection and effective treatment, significantly reducing the risks associated with these conditions.
Brain Aneurysms
Causes & Risk Factors
Aneurysms develop due to thinning or weakening of artery walls. Contributing factors include:
-
High blood pressure
-
Smoking
-
Family history of aneurysms
-
Atherosclerosis (hardening of arteries)
-
Traumatic brain injury
-
Certain inherited connective tissue disorders (e.g., Marfan or Ehlers-Danlos syndrome)
Symptoms
Many aneurysms remain silent until they leak or rupture.
Unruptured Aneurysm Symptoms (if large or pressing on nearby nerves):
-
Headache or eye pain
-
Double or blurred vision
-
Drooping eyelid
-
Weakness or numbness in the face
Ruptured Aneurysm Symptoms:
-
Sudden, severe “worst headache of my life”
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Stiff neck
-
Sensitivity to light
-
Seizures
-
Loss of consciousness
A ruptured aneurysm is a medical emergency that requires immediate intervention.
Arteriovenous Malformations (AVMs)
Causes
Most AVMs are congenital (present at birth), though the exact cause is unknown. They are often discovered incidentally or after a rupture.
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on the AVM’s location and size:
-
Headaches
-
Seizures
-
Weakness, numbness, or paralysis in part of the body
-
Vision or speech difficulties
-
Sudden neurological decline due to bleeding
Diagnosis
Early and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective management.
Common diagnostic tools include:
-
CT Scan: Quick detection of bleeding in emergencies
-
MRI: Detailed imaging of brain tissue and vascular malformations
-
CT/MR Angiography: Visualizes blood vessels to identify aneurysms or AVMs
-
Cerebral Angiography: A gold-standard test to map blood vessel structure before treatment
Treatment Options
For Brain Aneurysms
-
Endovascular Coiling:
A minimally invasive procedure where tiny coils are inserted through a catheter into the aneurysm to block blood flow and prevent rupture. -
Surgical Clipping:
A neurosurgeon places a small clip at the neck of the aneurysm to stop blood from entering it. -
Flow-Diverter Stents:
Used for certain aneurysms to redirect blood flow away from the weak area.
For AVMs
-
Microsurgical Removal (Resection):
Surgical removal of the AVM for accessible lesions. -
Endovascular Embolization:
A catheter-based procedure in which materials are injected into the AVM to block abnormal blood flow. -
Stereotactic Radiosurgery (Gamma Knife / CyberKnife):
A focused, high-dose radiation treatment to shrink or close small AVMs over time.
Often, a multimodal approach—combining two or more of these treatments—is used for best results.
Recovery and Aftercare
-
Hospital Stay: Varies depending on the procedure and the patient’s condition (typically a few days to two weeks for ruptured cases).
-
Rehabilitation: Physical therapy, speech therapy, or occupational therapy may be needed for patients recovering from hemorrhage or surgery.
-
Lifestyle Adjustments: Controlling blood pressure, avoiding smoking, and following a healthy lifestyle to prevent recurrence.
-
Regular Follow-Up: Imaging tests and clinical evaluations to ensure long-term safety and monitor for recurrence.
Why Choose Us
-
Specialized Expertise: Extensive experience in managing complex brain aneurysms and AVMs, including ruptured emergencies.
-
Advanced Endovascular & Microsurgical Techniques: State-of-the-art facilities for minimally invasive and precision-guided treatments.
-
Comprehensive Emergency Care: 24/7 readiness for urgent intervention to save lives and reduce neurological damage.
-
Multidisciplinary Approach: Collaboration among neurosurgeons, neuro-interventional radiologists, critical care specialists, and rehabilitation experts.
-
Patient-Centered Care: Compassionate guidance for patients and families from diagnosis through recovery.